Science
(www.olympiadsuccess.com)
Chapter 11: Human Eye and Colorful World
Class: X
Exercises
Question 1
The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
Answer 1
Question 2
The human eye forms the image of an object at its:
Answer 2
Question 3
The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about
Answer 3
Question 4
The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
Answer 4
Question 5
A person needs a lens of power −5.5 diopters for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 diopter. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?
Answer 5
According to lens formula:
or
Question 6:
The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
Answer 6:

Question 7:
Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
Answer 7:
A person suffering from hypermetropia can see the distant object clearly but faces difficulty in seeing nearby objects clearly. This is because the eye lens focuses the incoming divergent rays beyond the retina. This vision defect can be corrected by using a convex lens.
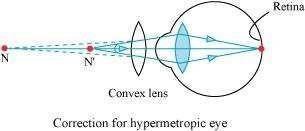

Question 8:
What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
Answer8:
The size of eyes cannot be increased or decreased, the image distance remains constant. When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, the increase in the object distance is compensated by the change in the focal length of the eye lens. The focal length of the eyes is changed in such a way that the image is always formed at the retina of the eye.
Question 9:
Why do stars twinkle?
Answer 9:
Stars twinkle due to the atmospheric refraction of light. The light coming from stars gets refracted at different levels because of the variation in the air density at different levels of the earth’s atmosphere. When the star light comes more towards us after refraction, it appears brighter than when it comes less towards us. Therefore, it appears as if the stars are twinkling at night.
Question 10:
Explain why the planets do not twinkle?
Answer 10:
Planets are closer to the earth and planets appear larger in comparison with the stars. The light coming from planets does not bend much when it enters into earth atmosphere. Therefore, it appears that planets do not twinkle.
Question 11:
Why does the Sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Answer 11:
The light rays coming from the Sun travel a greater distance in the earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes during sunrise. In this journey, the shorter wavelengths of lights are scattered out and only longer wavelengths reach our eyes. The red colour is able to reach our eyes as it has a longer wavelength, and that is why the Sun appears reddish early in the morning.
Question 12:
Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Answer 12:
The sky appears blue to us because scattering happens due to the particles in the atmosphere. There is no atmosphere in the outer space and in absence of atmosphere the sunlight that reach to astronaut is not scattered and hence is appears dark to them instead of blue.
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.
Explore More
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.
Explore More
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.
Explore More
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.
Explore More
Online tuitions for international compeitions like SASMO, SEAMO, etc for Grades 1-11.
Explore More