Science
(www.olympiadsuccess.com)
Chapter 10: Reflection and Refraction
Class: X
Exercises
Question 1
Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
(a) Water
(b) Glass
(c) Plastic
(d) Clay
Answer 1
(d) Clay because a lens allows light to pass through it and light cannot pass through clay. It cannot be used to make a lens.
Question 2
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the
object. Where should be the position of the object?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Answer 2
(d) the image formed is virtual, erect, and larger than the object when an object is placed between the pole and principal focus of a concave mirror.
Question 3
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size
of the object?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
Answer 3
(b) at twice the focal length
Question 4
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of −15 cm. The mirror
and the lens are likely to be
(a) both concave
(b) both convex
(c) the mirror is concave, and the lens is convex
(d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
Answer 4
(a) both concave. Because the focal length of a concave mirror and a concave lens are taken as negative.
Question 5
No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) plane
(b) concave
(c) convex
(d) either plane or convex.
Answer 5
(d) Either plane or convex. Because image formed in a convex mirror and plane mirror is always virtual and erect.
Question 6
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
Answer 6
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm. For reading small letters a convex lens with shorter focal length is preferred because magnification is more in such convex lenses.
Question 7
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15
of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show
the image formation in this case.
Answer 7
Given, focal length of concave mirror = 15 cm.
In a concave mirror an erect image if formed when an object is placed between its pole (P) and
the principal focus (F).
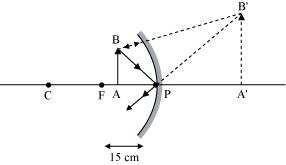
Therefore, the object must be placed anywhere between the pole and 15 cm (focal length) to obtain an erect image of an object. The image formed will be larger than the object.
Question 8
Name the type of mirror used in the following situations.
(a) Headlights of a car
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle
(c) Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
Answer 8
Question 9
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations
Answer 9
A complete will be formed from a convex lens when it’s one half is covered with black paper.
Case When the upper half of the lens is covered
When the upper half of the lens is covered, a ray of light coming from the object will be refracted by the lower half of the lens. The refracted rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the complete image of the given object.
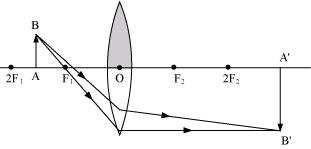
Case When the lower half of the lens is covered
When the lower half of the lens is covered, a ray of light coming from the object is refracted by the upper half of the lens. The refracted rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the complete image of the given object.
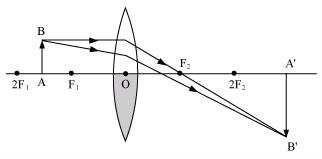
Question 10
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm.
Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Answer 10

Ray diagram
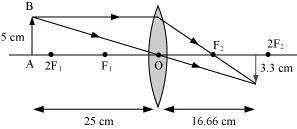
Question 11
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the
object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Answer 11

Ray diagram
Question 12
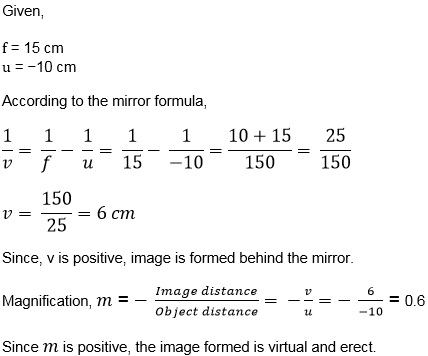
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm.
Find the position and nature of the image.
Answer 12
Question 13
The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean?
Answer 13

Question 14
An object 5.0 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of
radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Answer 14

Question 15
An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18
image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Answer 15
Object distance, u = −27 cm
Object height, h = 7 cm
Focal length, f = −18 cm

Question 16
Find the focal length of a lens of power −2.0 D. What type of lens is this?
Answer 16
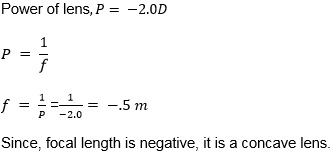
Question 17
A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the
lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
Answer 17

Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.
Explore More
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.
Explore More
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.
Explore More
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.
Explore More
Online tuitions for international compeitions like SASMO, SEAMO, etc for Grades 1-11.
Explore More