Science
(www.olympiadsuccess.com)
Chapter 6: Tissues
Class: IX
Exemplar sheet 6
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
Answer 1
(b)
Question 2
Find out incorrect sentence
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
(d) Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles
Answer 2
(c)
Question 3
Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem
Answer 3
(b)
Question 4
Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
Answer 4
(b)
Question 5
Intestine absorb the digested food materials. What type of epithelial cells
are responsible for that?
(a) Stratified squamous epithelium
(b) Columnar epithelium
(c) Spindle fibres
(d) Cuboidal epithelium
Answer 5
(b)
Question 6
A person met with an accident in which two long bones of hand were dislocated. Which among the following may be the possible reason?
(a) Tendon break
(b) Break of skeletal muscle
(c) Ligament break
(d) Areolar tissue break
Answer 6
(c)
Question 7
While doing work and running, you move your organs like hands, legs etc.
Which among the following is correct?
(a) Smooth muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones
(b) Smooth muscles contract and pull the tendons to move the bones
(c) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones
(d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones
Answer 7
(d)
Question 8
Which muscles act involuntarily?
(i) Striated muscles
(ii) Smooth muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles
(iv) Skeletal muslces
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer 8
(c)
Question 9
Meristematic tissues in plants are
(a) localised and permanent
(b) not limited to certain regions
(c) localised and dividing cells
(d) growing in volume
Answer 9
(c)
Question 10
Which is not a function of epidermis?
(a) Protection from adverse condition
(b) Gaseous exchange
(c) Conduction of water
(d) Transpiration
Answer 10
(c)
Question 11
Select the incorrect sentence
(a) Blood has matrix containing proteins, salts and hormones
(b) Two bones are connected with ligament
(c) Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile
(d) Cartilage is a form of connective tissue
Answer 11
(c)
Question 12
Cartilage is not found in
(a) nose
(b) ear
(c) kidney
(d) larynx
Answer 12
(c)
Question 13
Fats are stored in human body as
(a) cuboidal epithelium
(b) adipose tissue
(c) bones
(d) cartilage
Answer 13
(b)
Question 14
Bone matrix is rich in
(a) fluoride and calcium
(b) calcium and phosphorus
(c) calcium and potassium
(d) phosphorus and potassium
Answer 14
(b)
Question 15
Contractile proteins are found in
(a) bones
(b) blood
(c) muscles
(d) cartilage
Answer 15
(c)
Question 16
Voluntary muscles are found in
(a) alimentary canal
(b) limbs
(c) iris of the eye
(d) bronchi of lungs
Answer 16
(b)
Question 17
Nervous tissue is not found in
(a) brain
(b) spinal cord
(c) tendons
(d) nerves
Answer 17
(c)
Question 18
Nerve cell does not contain
(a) axon
(b) nerve endings
(c) tendons
(d) dendrites
Answer 18
(c)
Question 19
Which of the following helps in repair of tissue and fills up the space inside the organ?
(a) Tendon
(b) Adipose tissue
(c) Areolar
(d) Cartilage
Answer 19
(c)
Question 20
The muscular tissue which function throughout the life continuously without fatigue is
(a) skeletal muscle
(b) cardiac muscle
(c) smooth muscle
(d) voluntary muscle
Answer 20
(b)
Question 21
The muscular tissue which function throughout the life continuously
without fatigue is
(a) skeletal muscle
(b) cardiac muscle
(c) smooth muscle
(d) voluntary muscle
Answer 21
(d)
Question 22
The dead element present in the phloem is
(a) companion cells
(b) phloem fibres
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) sieve tubes
Answer 22
(b)
Question 23
Which of the following does not lose their nucleus at maturity?
(a) Companion cells
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Vessel
(d) Sieve tube cells
Answer 23
(a)
Question 24
In desert plants, rate of water loss gets reduced due to the presence of
(a) cuticle
(b) stomata
(c) lignin
(d) suberin
Answer 24
(a)
Question 25
A long tree has several branches. The tissue that helps in the side ways conduction of water in the branches is
(a) collenchyma
(b) xylem parenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) xylem vessels
Answer 25
(d)
Question 26
If the tip of sugarcane plant is removed from the field, even then it keeps on growing in length. It is due to the presence of
(a) cambium
(b) apical meristem
(c) lateral meristem
(d) intercalary meristem
Answer 26
(d)
Question 27
A nail is inserted in the trunk of a tree at a height of 1 metre from the
ground level. After 3 years the nail will
(a) move downwards
(b) move upwards
(c) remain at the same position
(d) move sideways
Answer 27
(c)
Question 28
Parenchyma cells are
(a) relatively unspecified and thin walled
(b) thick walled and specialised
(c) lignified
(c) none of these
Answer 28
(a)
Question 29
Flexibility in plants is due to
(a) collenchyma
(b) sclerenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) chlorenchyma
Answer 29
(a)
Question 30
Cork cells are made impervious to water and gases by the presence of
(a) cellulose
(b) lipids
(c) suberin
(d) lignin
Answer 30
(c)
Question 31
Survival of plants in terrestrial environment has been made possible by the presence of
(a) intercalary meristem
(b) conducting tissue
(c) apical meristem
(d) parenchymatous tissue
Answer 31
(b)
Question 32
Choose the wrong statement
(a) The nature of matrix differs according to the function of the tissue
(b) Fats are stored below the skin and in between the internal organs
(c) Epithelial tissues have intercellular spaces between them
(d) Cells of striated muscles are multinucleate and unbranched
Answer 32
(c)
Question 33
The water conducting tissue generally present in gymnosperm is
(a) vessels
(b) sieve tube
(c) tracheids
(d) xylem fibres
Answer 33
(c)
Short Answer Questions
Question 34
Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have thicker layer of subcutaneous fat. Describe why?
Answer 34
Hint— Fat acts as subcutaneous insulation of body for thermoregulation
Question 35
Match the column (A) with the column (B)
(A) (B)
(a) Fluid connective tissue (i) Subcutaneous layer
(b) Filling of space inside the organs (ii) Cartilage
(c) Striated muscle (iii) Skeletal muscle
(d) Adipose tissue (iv) Areolar tissue
(e) Surface of joints (v) Blood
(f) Stratified squamous epithelium (vi) Skin
Answer 35
a—v; b—iv; c—iii; d—i; e—ii; f—vi;
Question 36
Match the column (A) with the column (B)
(A) (B)
(a) Parenchyma (i) Thin walled, packing cells
(b) Photosynthesis (ii) Carbon fixation
(c) Aerenchyma (iii) Localized thickenings
(d) Collenchyma (iv) Buoyancy
(e) Permanent tissue (v) Sclerenchyma
Answer 36
a—i; b—ii c—iv; d—iii; e—v;
Question 37
If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of glass jar. Explain why?
Answer 37
Hint—Because of transpiration
Question 38
Name the different components of xylem and draw a living component?
Answer 38
Hint—Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
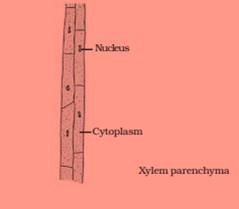
Question 39
Draw and identify different elements of phloem.
Answer 39
Hint—Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma.
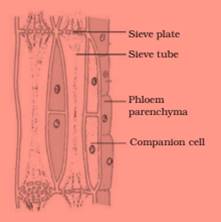
Section of Phloem
Question 40
Write true (T) or false (F)
(a) Epithelial tissue is protective tissue in animal body.
(b) The lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made up of epithelial tissue.
(c) Epithelial cells have a lot of intercellular spaces.
(d) Epithelial layer is permeable layer.
(e) Epithelial layer does not allow regulation of materials between body and external environment.
Answer 40
(a)—T, (b)—T, (c)—F, (d) —T, (e)—F
Question 41
Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each type.
Answer 41
Voluntary muscles can be moved consciously when we want them to move. For example, skeletal muscles or muscles of limbs. Involuntary muscles function I under unconscious control. We cannot start or stop them from working by our desire. examples are cardiac muscles and smooth muscles.
Question 42
Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary (V) or involuntary (I V) muscles.
(a) Jumping of frog
(b) Pumping of the heart
(c) Writing with hand
(d) Movement of chocolate in your intestine
Answer 42
(a)—V, (b)—I V, (c)—V, (d) —I V
Question 43
Fill in the blanks
(a) Lining of blood vessels is made up of———.
(b) Lining of small intestine is made up of ———.
(c) Lining of kidney tubules is made up of———.
(d) Epithelial cells with cilia are found in———of our body.
Answer 43
(a) squamous epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) cuboidal epithelium
(d) respiratory tract
Question 44
Water hyacinth float on water surface. Explain.
Answer 44
Hint— Due to aerenchyma present in the swollen petiole.
Question 45
Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites?
Answer 45
Hint- Epidermis having thick cuticle and waxy substances to prevent the invasion of parasites.
Question 46
Fill in the blanks
(a) Cork cells possesses———on their walls that makes it impervious to gases and water.
(b) ——— have tubular cells with perforated walls and are living in nature.
(c) Bone possesses a hard matrix composed of———and ———.
Answer 46
(a) suberin (b) sieve tubes (c) calcium and phosphorus
Question 47
Why is epidermis important for the plants?
Answer 47
Hint—Epidermis is important for plants due to the following reasons
(i) it gives protection
(ii) helps in gaseous exchange
(iii) checks water loss
(iv) root hairs arising from epidermis helps in absorption of water and minerals.
Question 48
Fill in the blanks
(a) ———are forms of complex tissue.
(b) ———have guard cells.
(c) Cells of cork contain a chemical called———
(d) Husk of coconut is made of ———tissue.
(e) ———gives flexibility in plants.
(f) ———and———are both conducting tissues.
(g) Xylem transports———and———from soil.
(h) Phloem transport———from———to other parts of the plant.
Answer 48
(a) Xylem and phloem
(b) Stomata
(c) Suberin
(d) Sclerenchyma
(e) Collenchyma
(f) Xylem; phloem
(g) Water; minerals
(h) food; leaf
Long Answer Questions
Question 49
Differentiate between sclerenchyma and parenchyma tissues. Draw well labelled diagram.
Answer 49
Differences between parenchyma and sclerenchyma.

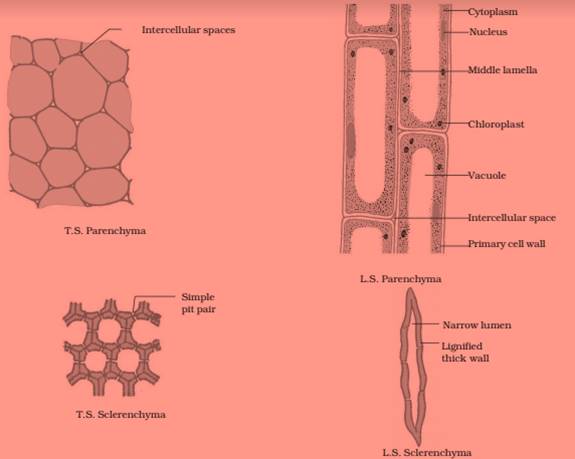
Question 50
Describe the structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues. Draw diagram of each type of epithelial tissue.
Answer 50
Epithelial tissues are the covering or protective tissues in the animal body. Epithelium covers most organs and cavities within the body and keep different body systems separate. The examples of epithelial tissue are the lining of blood vessels, skin, lung alveoli and kidney tubules , the lining of the mouth etc... Cells in epithelial tissue are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. They have only a small amount of cementing material between them and almost no intercellular spaces. The permeability of various epithelial cells play an important role in regulating the exchange of materials between the body and the external environment and also between different parts of the body. Cells of all epithelium are usually separated from the underlying tissue by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane.
Epithelial tissues are of following types— (1) Simple squamous epithelium (2) Stratified squamous epithelium (3) Columnar epithelium, and (4) Cubodial epithelium. These tissues differ in structure that correlate with their unique functions. For example, we can see simple flat kind of epithelium in cells lining blood vessels or lung alveoli, where transportation of substances occurs through a selectively permeable surface. This is called the simple squamous epithelium. The cells of simple squamous epithelium are extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining. The oesophagus ,skin, and the lining of the mouth are also covered with the squamous epithelium. Skin epithelial cells are arranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear. Since, they are arranged in layers, the epithelium is called stratified squamous epithelium.
Tall epithelial cells are present in region where secretion , absorption etc occur, as in the inner lining of the intestine. This columnar epithelium facilitatesmovement across the epithelial barrier. In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which are hair-like projections on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells. These cilia can move, and their movement pushes the mucus forward to clear it. This type of epithelium is thus ciliated columnar epithelium.
Cuboidal epithelium forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands, where it provides mechanical support. Some of the cuboidal or columnar cells are specialized for purpose of secretion and such cell is called glandular epithelium.
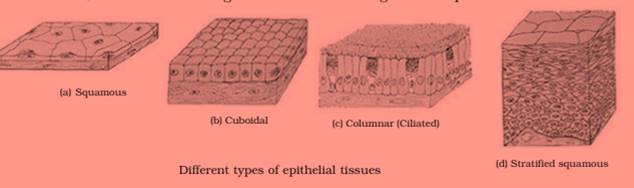
Question 51
Draw well labelled diagrams of various types of muscles found in human body.
Answer 51
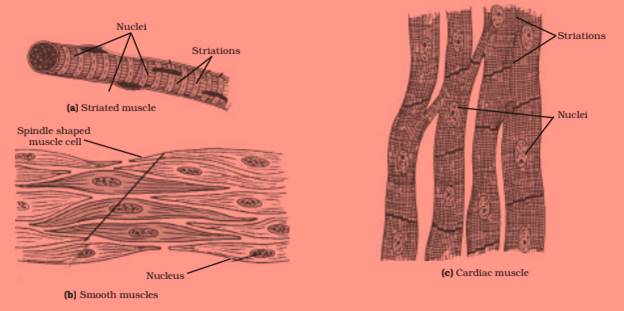
Question 52
Give reasons for
(a) Meristematic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they lack vacuole.
(b) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues.
(c) We get a crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
(d) Branches of a tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity.
(e) It is difficult to pull out the husk of a coconut tree.
Answer 52
Hint—
(a) No need of storage.
(b) Because they are lignified.
(c) Presence of stone cells (sclerenchyma)
(d) Presence of Collenchyma.
(e) Sclerenchyma.
Question 53
List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? Mention their role.
Answer 53
Characteristics
a)
They are impervious to gases and water.
Question 54
Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues? How are they different from one other?
Answer 54
Both xylem and phloem consist of more than one type of cells, which coordinate to perform a common function.

Question 55
(a) Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants
(b) Define the process of differentiation
(c) Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Answer 55
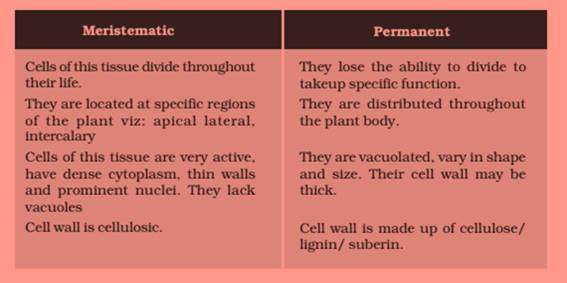
(b) The loss of ability to divide by taking up a permanent shape, size and function is called differentiation.
(c) Simple: Parenchyma/collenchyma/sclerenchyma
Complex: Phloem/xylem
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.
Explore More
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.
Explore More
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.
Explore More
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.
Explore More
Online tuitions for international compeitions like SASMO, SEAMO, etc for Grades 1-11.
Explore More