Science
(www.olympiadsuccess.com)
Chapter 9: Soil
Class VII
NCERT Questions
Question 1
In addition to the rock particles, the soil contains (i) air and water (ii) water and plants (iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water (iv) water, air and plants
Answer 1
(iii) minerals, organic matter, air and water.
Question 2
The water holding capacity is the highest in (i) sandy soil (ii) clayey soil (iii) loamy soil (iv) mixture of sand and loam
Answer 2
(ii) clayey soil
Question 3
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
Column I Column II
(i) A home for living organisms (a) Large particles
(ii) Upper layer of the soil (b) All kinds of soil
(iii) Sandy soil (c) Dark in colour
(iv) Middle layer of the soil (d) Small particles and packed tight
(v) Clayey soil (e) Lesser amount of humus
Answer 3
Column I Column II
(i) A home for living organisms (b) All kinds of soil
(ii) Upper layer of the soil (c) Dark in colour
(iii) Sandy soil (a) Large particles
(iv) Middle layer of the soil (e) Lesser amount of humus
(v) Clayey soil (d) Small particles and packed tight
Question 4
Explain how soil is formed.
Answer 4
Soil is formed by weathering of rocks. Weathering is the breakdown of rocks by the action of air, wind and water. Soil formation is a slow process. It occurs all the time. Soil formation is a two-step process:
Weathering of rocks takes place. Rock is broken down into small particles.
These small particles mix with humus (organic matter) and form soil.
Question 5
How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Answer 5
Clayey soil is rich in humus and are very fertile, so it is suitable for growing cereals like wheat and gram. Such soil is good at retaining water. For paddy, soils rich in clay and organic matter and having a good capacity to retain water are ideal. For lentils (masoor) and other pulses, loamy soils, which drain water easily, are required.
Question 6
List the differences between clayey soil and sandy soil.
Answer 6
sticky and wet. through the soil.
wheat and gram. cotton cultivation.
Question 7
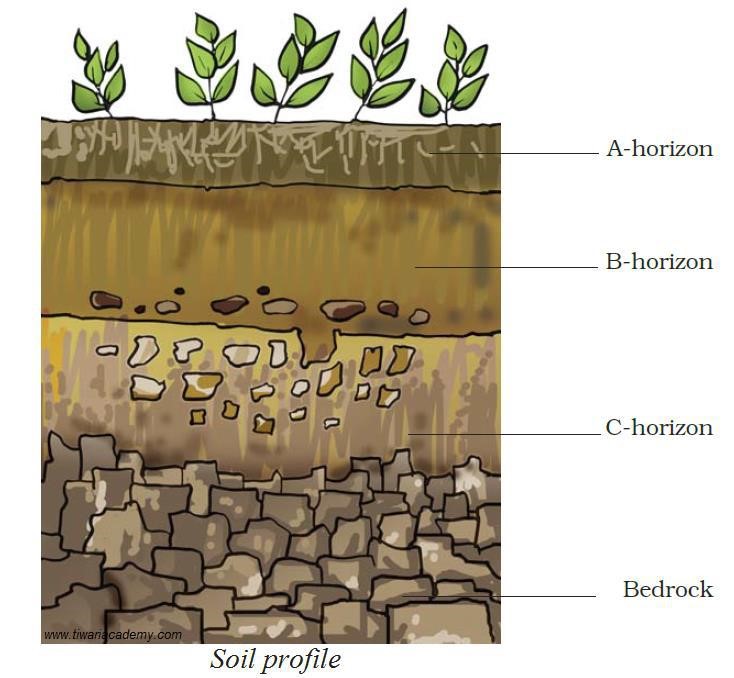
Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers.
Answer 7
A vertical section through different layers of the soil is called the soil profile. Each layer differs in feel (texture), colour, depth and chemical composition. These layers are referred to as horizons.
The uppermost horizon is generally dark in colour as it is rich in humus and minerals. The humus makes the soil fertile and provides nutrients to growing plants. This layer is generally soft, porous and can retain more water. It is called the topsoil or the A-horizon.
The next layer has a lesser amount of humus but more of minerals. This layer is generally harder and more compact and is called the B-horizon or the middle layer.
The third layer is the C-horizon, which is made up of small lumps of rocks with cracks and crevices.
Below this layer is the bedrock, which is hard and difficult to dig with a spade.
Question 8
Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation. She observed that it took 40 min for 200 mL of water to percolate through the soil sample. Calculate the rate of percolation.
Answer 8:
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.
Explore More
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.
Explore More
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.
Explore More
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.
Explore More
Online tuitions for international compeitions like SASMO, SEAMO, etc for Grades 1-11.
Explore More